The concept known today as the Dark Web set its foundation in the early 2000s. In March of 2000, Freenet was released to allow a censorship-resistant way to use the Web. It also opened the way for sharing illegal pornographic material and pirated data. One of the key tools used on the Dark Web today was first released in 2002 – Tor, The Onion Router. Users gain greater anonymity online when using Tor because it encrypts Internet traffic and passes through several nodes.
What Is The Primary Difference Between The Deep Web And The Dark Web?
For business leaders, the strategic value lies in securing internal assets while gaining early threat awareness—all within legal and ethical frameworks. The real dangers of dark web vs deep web emerge when threat actors share stolen credentials, sell malware, and orchestrate attacks in hidden forums. Once data or tools reach this space, it can fuel large-scale campaigns. The Darknet is a subset of the Internet operating over encrypted, anonymous overlay networks that require special software like Tor, Freenet, or I2P.
Collecting Threat Intelligence
It has its own deep web, as dark web websites come with user accounts and other private areas. Tor can be used to visit everyday internet websites, but it also has numerous hidden websites and services which can’t be accessed on the regular internet. Tor powers them using its protocol known as Tor Hidden Service Protocol. And the websites limited to the Tor network have a special .onion address.
Why Dark Web Monitoring Is Important For Security Operations?
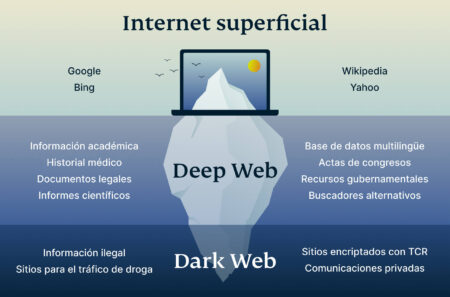
For instance, your Gmail inbox and your Google Drive are part of the deep web because they don’t exist as publicly accessible domains. Other examples include your bank account page and the settings page of your social media account, the admin page of your blog, and some academic journals. These websites exist in directories that Google (and other search engines) are barred from crawling. The dark web refers to encrypted online content that is not indexed by conventional search engines. Darknet provides a user with anonymity but service was introduced that allowed someone to host a website on the darknet and remain anonymous.
August’s Top VPN Discounts
To make your accounts as secure as they can be, make sure you’re not reusing or using variations of the same password across multiple accounts. With Pipeline, you leverage our cutting-edge Security Intelligence Vision. This proactive approach means you stay ahead of cybercriminals, protecting your digital assets from being compromised. As we navigate the deep and dark web, the distinctions between their uses, threats, and implications for businesses become starkly clear. At Pipeline, we arm your business against the unseen dangers lurking in the cyber shadows. The dark net also harbors illegal websites where cybercrime thrives.
Potential Risks
From a cyber-security perspective, it can be if you don’t know how to protect yourself. Non-technical people who are interested in satisfying their curiosity can quickly get into trouble. As such, you shouldn’t go looking around this area of the web unless you’re prepared and know what you’re doing.
- For instance, your Gmail inbox and your Google Drive are part of the deep web because they don’t exist as publicly accessible domains.
- The sorts of illegal activities and documents named in these awards are bought, sold, and hosted via the dark web.
- The dark web isn’t all illicit deals and seedy undertakings; it’s used for an array of purposes.
- Before you go exploring the dark web, it’s crucial to recognize that it is much more dangerous than the surface web — and not just because of all the illegal activity happening on the dark web.
Dark Web illegal activities can lead to severe legal actions, such as arrest, and so it must be taken very seriously by the users. Popularly known as the visible web or indexed web is a unit of the WWW (World Wide Web) that is open for general usage and can be accessible by anyone around the world. To access this, one must have a working Internet connection and will also require a search engine (such as Google, Bing, etc.) to access the content. For example, in 2016, investigative news outlet ProPublica launched a hidden version of its website on the dark web to provide a secure and anonymous way for readers to access its content. This initiative aimed to protect the privacy of individuals in repressive regimes or those concerned about surveillance, allowing them to read news without exposing their identity.
You need the proper credentials to get in; even web crawlers are blocked from taking a peek. With only about 4 percent of all online content freely accessible (making up the surface web), the remainder is tucked away in the deep web. This means there is no easy, direct way for the general public to search this vast amount of unindexed content. In some cases, websites use various methods to block spiders and prevent indexing. These methods include using CAPTCHAs, multiple IP addresses for the same content, non-HTML content or data that spiders cannot pick up, password protection, and unlinked content. It also includes paywalled services such as video on demand and some online magazines and newspapers.
Common Content
One must always respect the laws and regulations regarding privacy. The surface web, which is also called the visible web and the open web, is any website that search engines can add to their database. This includes websites, blogs, online product listings, and even public posts on social media. The dark web’s anonymity draws users who need private communication, want to share sensitive information, or seek access to content censored in certain regions. But while it can support legitimate uses such as whistleblowing or journalistic sources, it’s also a hub for illegal activity.
However, the Dark Web isn’t all bad, and, in fact, the technology that makes it possible, Tor, was originally created by the U.S. government for legitimate purposes. The Surface Web, which is accessible via search engines like Google and Bing, only makes up a small portion of the Internet. The Deep and Dark Web lay outside the publicly accessible portions of the Internet and are used for different purposes. The risks of the dark web come when you aren’t careful with what you access. One of the most significant barriers to finding deep and dark web sources is that you must use the exact URL to access sources that are not indexed — even with a browser like Tor. For example, to access the popular dark web forum CryptBB, you must know the exact onion link; conducting a web search for the forum will not turn up anything useful.
No, you cannot access the dark web through a regular browser, like Google Chrome, Firefox, etc. There are specialized browsers that are meant for dark web browsing like Tor browser and Whonix. The dark web gained traction for its association with individuals engaging in illicit activities like the trading of illegal goods and services, coordinating attacks, drug trafficking, and more. Start a free 30-day trial of Keeper Password Manager today to begin securing your accounts from common cyber threats on all parts of the internet. One dark web monitoring tool that works alongside Keeper Password Manager is BreachWatch®. BreachWatch monitors for suspicious activity on the dark web and alerts you as soon as any dark web activity matches the credentials stored in your Keeper Vault.

The person or group who has posted a webpage on the open web doesn’t care who has access to it or what can be done with it. To use a real-world example, you probably don’t care who in a large group knows your name or the color of your hair. The concept of the internet as a network that can host many different types of network applications is important to grasp if you want to understand the difference between deep, dark, and surface webs. The “Deep Web” and “Dark Web” both sound intimidating, but that doesn’t mean they’re the same thing. While they’re related, knowing the difference can keep you safe from dangerous places on the internet and make you a hit at parties. There are a lot of misconceptions about it, but we’ll answer that question once and for all in this guide.
The vast majority of the internet exists outside the realm of a Google search, and the first layer below the surface-level internet is what is called the deep web. As with many things in life, the things we believe ourselves to be most familiar with are the least known to us. It’s where our daily online activities take place, and what most people consider to be the Internet. This over familiarity with it gives us a sense that we understand what it is and how it works, because, well, it works. In addition, just surfing the dark web can unleash malware on your computer. Besides, governments might actively monitor such activity, and anyone showing a keen interest in the dark web can become a law enforcement target.
Also, these sites are often linked to publicly accessible pages, making them findable and accessible by users with the right login credentials and willingness to pay. For example, sites like Netflix are reachable from search engines, but the videos hosted on the site are only accessible to users who have created an account and paid a subscription fee. The deep web is a layer of the internet that’s not indexed by search engines and requires further permissions to access, like a paywalled academic resource or an employee-only corporate website. The dark web is another layer of the internet where users are anonymous and illegal activities, such as drugs or weapons trading, may occur. The most popular dark web network is The Onion Network (TOR network). There are several others, but none with as large a user base as TOR.



